

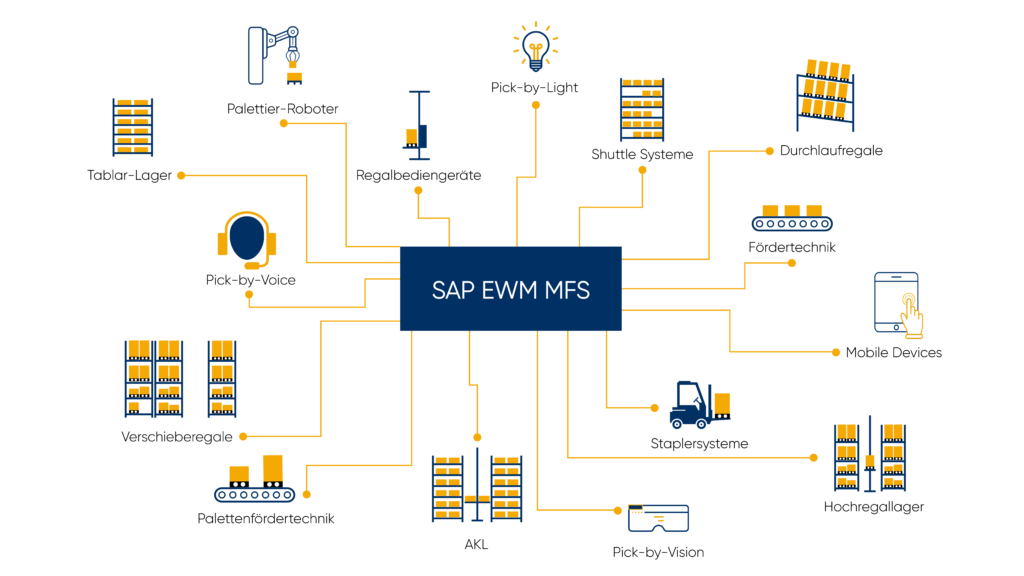
What is SAP EWM MFS?
SAP EWM MFS is a fully integrated functional component of SAP Extended Warehouse Management (SAP EWM). With the material flow system (MFS), automated warehouses can be connected to SAP Extended Warehouse Management (EWM) without an additional warehouse control computer. External middleware and subsystems, such as warehouse control computers or material flow computers (MFR), are thus completely eliminated. Reducing the complexity of the interfaces involved results in lower operating costs and therefore maximises investment protection.
Communication
Communication between SAP EWM MFS (Material Flow System) and a PLC (programmable logic controller) takes place directly via TCP/IP, i.e. without middleware.
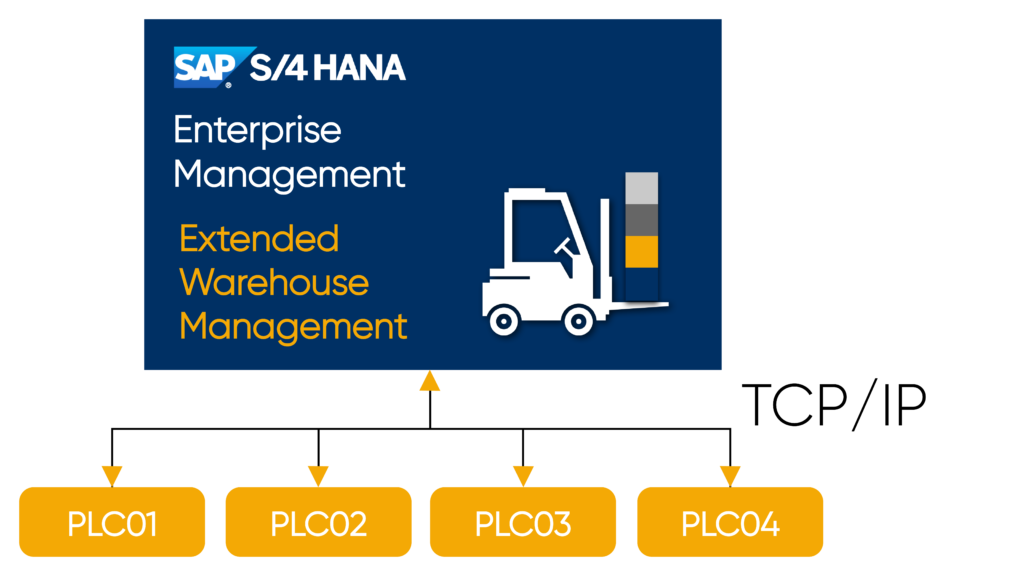
The telegrams, which represent a character string with many fields, are exchanged via a socket connection. Both a bidirectional connection via a single channel and a multi-channel connection with one send and one receive channel are possible. SAP EWM MFS (Material Flow System) always acts as a TCP client, i.e. SAP EWM MFS actively establishes the connection to the PLC (programmable logic controller). An uninterrupted connection is ensured via LIVE telegrams, which are exchanged regularly.
System landscape
The SAP EWM MFS (Material Flow System) component is included in the SAP EWM Advanced (Extended Warehouse Management) product. SAP EWM MFS can be used both in an integrated SAP EWM and in a decentralised scenario.
Automatic trades and processes
High-bay warehouse (HRL)
With SAP Material Flow System (SAP EWM MFS), automated high-bay warehouses of all kinds are directly connected, controlled and optimised. The movement commands are transferred in real time to the PLC (programmable logic controller) of the storage and retrieval machines. Complex storage and retrieval strategies as well as optimisations such as equal distribution of items across all aisles, route-optimised storage location determination, double or multiple-deep storage, curve walkers or double cycles are carried out entirely in SAP EWM MFS.
Automated small parts warehouse (AKL)
Automated small parts warehouses for containers, trays and vertical lift systems are connected and controlled directly with SAP EWM MFS (Material Flow System). The multi-deep storage frequently used in automated small parts warehouses combined with multiple LAMs (load handling devices) are fully mapped in SAP EWM MFS. The transport orders, often in the form of half cycles (2-step orders), are transferred in real time to the PLC (programmable logic controller) of the storage and retrieval machines.
Multiple-deep storage
Specific putaway strategies are mapped in SAP MFS (SAP Material Flow System) for multiple-deep warehouses, for example to minimise the probability of stock transfer. Handling units close to the aisle are reserved for stock removal and the stock removal strategy takes pair formation into account wherever possible. Many projects with double-deep and multiple-deep storage for high-bay warehouses and miniload warehouses have already been successfully realised with SAP MFS (SAP Material Flow System). Multi-deep storage is also possible in combination with subdivided storage bays.
Subdivided storage bays (pallet behaviour)
In many high-bay warehouses, not only Euro pallets or only industrial pallets are stored, but several different pallet types at the same time. However, the positions within the high-bay warehouse should not be permanently assigned to a specific pallet type. Instead, wider storage bays are defined in which 3-5 pallets fit in width depending on the pallet type. For example, as soon as a Euro pallet is the first pallet to be stored in a storage bay, the storage bay is logically subdivided so that further pallets of the same type can be stored. This logic, known as "pallet behaviour", is supported in SAP EWM in conjunction with SAP EWM MFS. Subdivided storage fields are also possible in combination with multiple-deep storage.
Conveyor systems
With SAP EWM MFS (Material Flow System), conveyor systems for pallets, containers etc. can be connected directly. The necessary conveyor paths are stored in the system as routes. Complex conveyor system layouts, such as those with buffers, sorting systems, multiple levels or winders, are mapped in SAP EWM MFS (Material Flow System) using routing control logic. Transport orders and time-critical decisions are transmitted to the conveyor systems in real time via direct communication with the PLC (programmable logic controller) with the required response time. Alternative routes allow the flow of goods to be rerouted quickly if parts of the conveyor line fail.
Automated guided vehicle systems (AGV)
In-plant conveyor systems such as automated guided vehicles (AGVs) are controlled directly by SAP EWM MFS (Material Flow System). Communication takes place either with the host computer of the AGV infrastructure or with each vehicle directly. Driving commands and feedback from the individual vehicles or the host computer are processed in real time.
Electric monorail systems (EMS)
In-plant conveyor systems such as electric monorail systems (EMS) are controlled directly by SAP EWM MFS (Material Flow System). Communication takes place with the master computer of the EMS infrastructure. Travel commands and feedback as well as time-critical decisions are processed in real time.
Electric floor conveyors (EBB)
In-plant conveyor systems such as the electric floor conveyors (EBB) are controlled directly by SAP EWM MFS (Material Flow System). Communication takes place with the master computer of the EBB infrastructure. Travel commands and feedback as well as time-critical routing decisions are processed in real time.
Goods-to-person (WzP, WzM)
The "goods-to-person" process (formerly: "goods-to-man" / WzM) maps the provision of articles on pallets or containers to the order picker. Automated high-bay warehouses and automated small parts warehouses are often equipped with goods-to-person picking stations that are optimally supplied by SAP EWM MFS (Material Flow System). Disposal, i.e. the return of goods from the picking stations back to the warehouse, is also coordinated by SAP EWM MFS. The user is supported and guided at the WzM workstation by configurable dialogues in SAP EWM (Extended Warehouse Management).
Pick-by-Light, Pick-to-Light
When picking small parts with high error prevention requirements, pick-by-light systems are generally used in combination with flow racks or totes. SAP EWM (Extended Warehouse Management) handles the assignment of the goods to be picked to the target bins in the process, while SAP EWM MFS (Material Flow System) forwards the pick orders to be processed to the pick-by-light system. SAP EWM and SAP EWM MFS can map and fully coordinate single-stage, multi-stage and parallel picking processes.
Labelling of load units
When goods are received, automated labelling systems are often used to apply labels to the load units to enable them to be identified later in the warehouse. Shipping labels can also be applied to the load units at goods issue using automated conveyor technology. SAP EWM MFS (Material Flow System) processes the signals from the conveyor system in real time and has SAP EWM (Extended Warehouse Management) generate the labels in good time and send them to the labelling systems at the right moment. The combination of SAP EWM and SAP EWM MFS enables the automation of labelling for incoming goods, outgoing goods and other warehouse processes.
Automated palletising
Automation is often used when palletising items from production. The products are prepared by layer palletisers or palletising robots according to a palletising scheme and placed on pallets. The products are then processed on the wrapper and labelled. Both layer palletisers and palletising robots can be connected directly to SAP EWM MFS (Material Flow System) with the appropriate interface. Depending on the degree of automation, SAP EWM MFS controls every single movement of the palletising robot or simply passes on the palletising scheme to it and only processes the feedback of successfully processed pallets.
How can we help you?
The special thing about CPRO conlog: Once the first functions for SAP EWM MFS (Material Flow System) have been implemented, they can already be tested. As the productive system and the associated automation systems are not normally available for test runs at this stage, CPRO conlog relies on virtual commissioning using the smartSim solution. The 3D simulation smartSim realistically simulates the behaviour of a productive PLC (programmable logic controller) and communicates with SAP EWM MFS via the same productive telegram interface. With the help of smartSim, even complex test scenarios and mass tests can be carried out with significantly less effort than on the productive system. The result is higher software quality and shorter project runtimes thanks to early testing and employee training opportunities.
CPRO conlog hands over the developments to the customer regularly and shortly after completion so that the customer has an early hands-on experience with the functions. This procedure not only serves to test the functions, but also to ensure acceptance by the company's employees.
- As-is analysis
- Support for target concept (specifications)
- Development of implementation concept (requirements specification)
- Implementation according to implementation concept
- Go-live support
- Advice on possible optimisations
- Virtual commissioning (smartSim)
Your advantages
- Smooth, safe and efficient material flow movements
- External middleware and subsystems are completely eliminated
- Reduction of interfaces
- Increased planning and investment security
- Two-stage SAP-PLC system architecture with end-to-end SAP integration possible
- Comprehensive mapping of all logistics processes in the warehouse and in the area of production supply
- Support and further development of SAP EWM / MFS are guaranteed in the long term

